Living with diabetes requires a thoughtful approach to nutrition. Food choices play a significant role in managing blood sugar levels, preventing complications, and promoting overall health. By focusing on nutrient-rich foods, individuals with diabetes can maintain stable blood sugar levels and improve their well-being. Here’s a comprehensive guide to building a healthy food list for diabetes management:
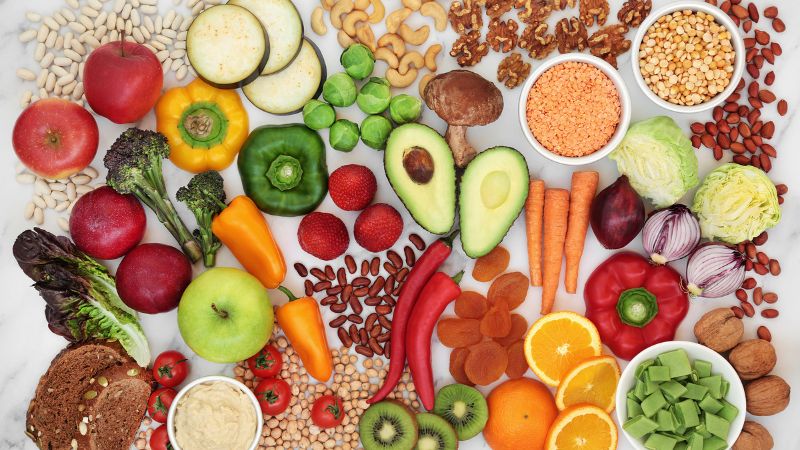
Non-Starchy Vegetables:
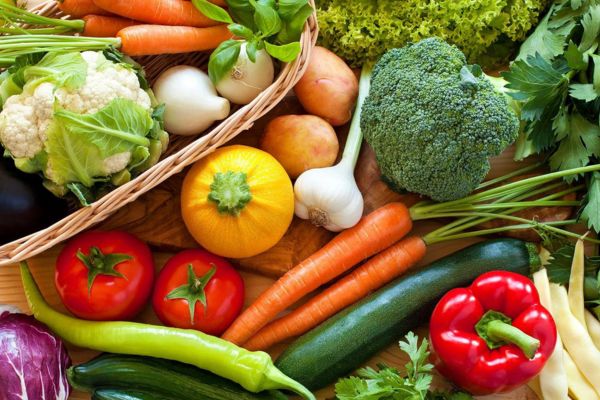

Leafy greens (spinach, kale, lettuce)
Broccoli
Cauliflower
Bell peppers
Cucumbers
Tomatoes
Brussels sprouts
Asparagus
Lean Proteins:
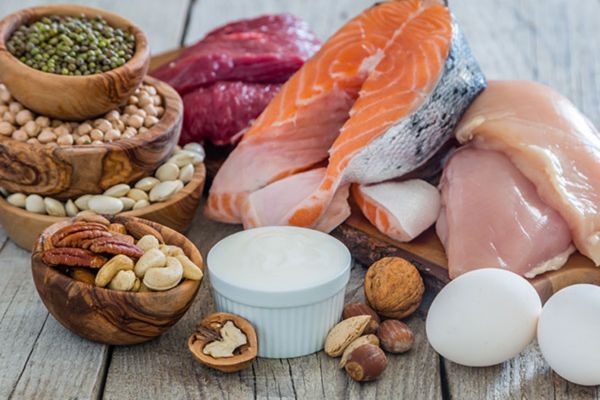

Skinless poultry (chicken, turkey)
Fish (salmon, tuna, mackerel)
Lean cuts of beef or pork
Tofu
Lentils
Beans (black beans, kidney beans, chickpeas)
Eggs
Healthy Fats:
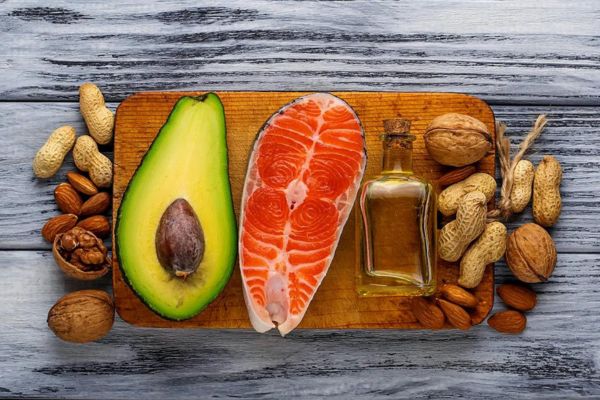

Avocado
Nuts (almonds, walnuts, pistachios)
Seeds (flaxseeds, chia seeds)
Olive oil
Coconut oil (in moderation)
Fatty fish (salmon, trout)
Whole Grains:

Quinoa
Brown rice
Whole wheat bread
Oats
Barley
Bulgur
Whole grain pasta
Low-Glycemic Fruits:
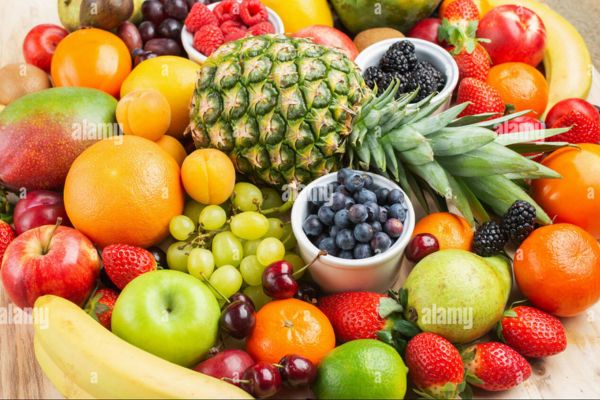

Berries (strawberries, blueberries, raspberries)
Apples
Pears
Citrus fruits (oranges, grapefruits)
Cherries
Plums
Peaches
Dairy or Dairy Alternatives:

Low-fat or non-fat yogurt
Skim milk
Unsweetened almond milk
Cottage cheese (low-fat)
Cheese (in moderation)
Herbs, Spices, and Flavorings:

Cinnamon
Turmeric
Garlic
Ginger
Basil
Rosemary
Thyme
Lemon juice
Beverages:

Water (plain or infused with fruits/herbs)
Herbal teas (green tea, chamomile)
Coffee (in moderation, without added sugar)
Sparkling water (plain or flavored, without added sugar)
Snacks:
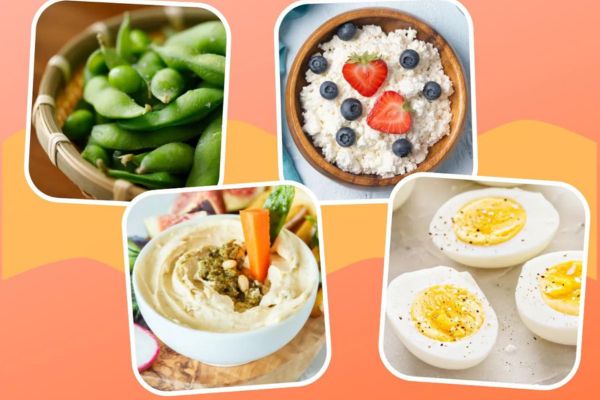

Raw vegetables with hummus
Greek yogurt with berries
Nuts and seeds
Cottage cheese with fruit
Air-popped popcorn
Hard-boiled eggs
Portion Control and Balanced Meals:

Be mindful of portion sizes to prevent overeating.
Aim for balanced meals that include a mix of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
Spread carbohydrate intake evenly throughout the day to help manage blood sugar levels.
Avoid or Limit:
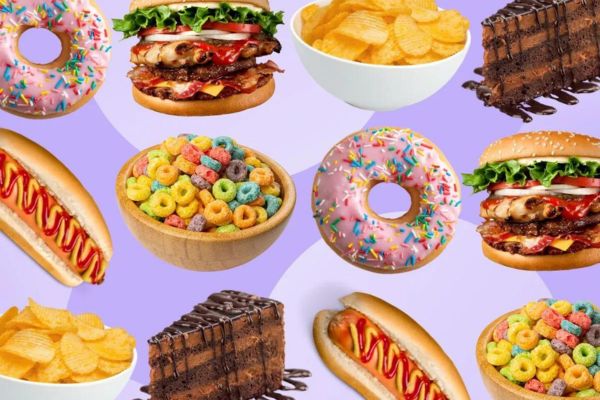

Sugary beverages (soda, fruit juice, sweetened coffee drinks)
Processed snacks and baked goods
Foods high in saturated and trans fats (fried foods, fatty cuts of meat, processed foods)
Excessive consumption of refined grains (white bread, white rice, sugary cereals)
High-sodium foods (canned soups, processed meats, salty snacks)
Conclusion
By incorporating these nutrient-rich foods into your diet and practicing portion control, you can effectively manage your diabetes while enjoying a diverse and satisfying array of meals. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to tailor your diet plan to your individual needs and preferences. With a focus on whole, unprocessed foods, you can nourish your body and thrive while living with diabetes.