Vitamin D, often referred to as the “sunshine vitamin,” is a crucial nutrient that plays a significant role in maintaining overall health and well-being. Essential for bone health, immune function, and various bodily processes, vitamin D can be obtained through exposure to sunlight, dietary sources, and supplements. Despite its importance, many people struggle to get enough vitamin D, leading to deficiencies that can impact health. Understanding the benefits and sources of vitamin D is key to ensuring you meet your daily needs and support your body’s vital functions.
Table of Contents
What is Vitamin D?
Vitamin D is a nutrient that your body needs for building and maintaining healthy bones. This is because calcium, the primary component of bone, can only be absorbed into the body when vitamin D is present.
How Does the Body Get Vitamin D?
Vitamin D can be obtained from several sources, including sunlight, food, and supplements. Here are the main sources of vitamin D:
1. Sunlight

Sun Exposure: The most natural and primary source of vitamin D. When your skin is exposed to ultraviolet B (UVB) rays from the sun, it produces vitamin D. Factors such as the time of day, geographic location, skin pigmentation, and use of sunscreen can influence how much vitamin D your body makes.
2. Food Sources of Vitamin D

Fatty Fish: Fish like salmon, mackerel, sardines, and tuna are rich in vitamin D.
Fish Liver Oils: Cod liver oil and fish oil are excellent sources of vitamin D.
Egg Yolks: Eggs contain small amounts of vitamin D, mainly in the yolk.
Beef Liver: Contains vitamin D but is also high in cholesterol.
Cheese: Provides small amounts of vitamin D.
Fortified Foods: Many foods are fortified with sources of vitamin D, including:
Cow’s milk and plant-based milks (such as soy, almond, and oat milk)
Orange juice
Cereals and oatmeal
Margarine and butter
3. Supplements

Vitamin D Supplements: Available in two forms, D2 (ergocalciferol) and D3 (cholecalciferol). D3 is more effective at raising and maintaining overall vitamin D levels.
Multivitamins: Many multivitamin preparations contain vitamin D.
Factors Affecting Vitamin D Production
Geographic Location: People living farther from the equator may not get enough UVB rays in winter months.
Skin Pigmentation: People with darker skin have more melanin, which can reduce the skin’s ability to produce vitamin D from sunlight.
Age: Older adults cannot produce vitamin D from sunlight.
Sunscreen Use: While important for protecting against skin cancer, sunscreen can reduce vitamin D production.
Benefits of Vitamin D

Bone Health: Vitamin D plays a crucial role in calcium absorption, promoting bone growth and remodeling. A deficiency can lead to bone disorders like osteoporosis in adults and rickets in children.
Immune Function: It helps regulate the immune system and reduce the risk of infections.
Mood and Mental Health: Adequate levels of vitamin D are linked to improved mood and may help in reducing the risk of depression.
Muscle Function: It is important for muscle function, and a deficiency can lead to muscle weakness and pain.
Signs of Vitamin D Deficiency
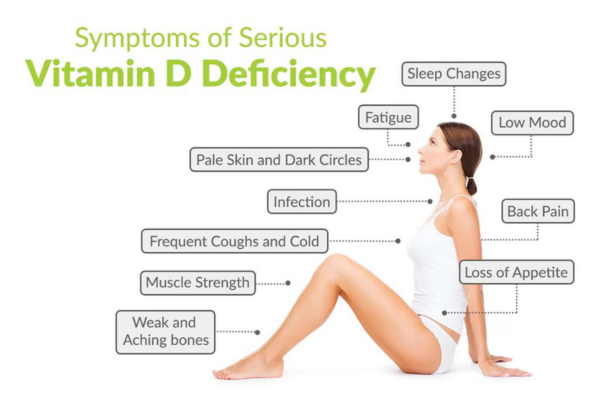
Bone Pain and Weakness: A common sign of deficiency is aching bones and muscle weakness.
Frequent Illnesses: Low vitamin D levels can lead to a weakened immune system.
Fatigue: Persistent tiredness or fatigue can be a symptom of low vitamin D levels.
Depression: Some studies have linked low vitamin D levels to mood disorders, including depression.
How Much Vitamin D Do You Need?
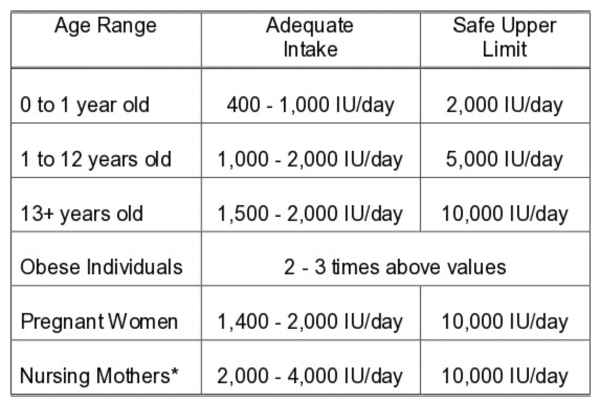
The amount of vitamin D you need depends on your age and health status:
Infants (0-12 months): 400 IU (International Units) per day
Children (1-18 years): 600 IU per day
Adults (19-70 years): 600 IU per day
Older Adults (71+ years): 800 IU per day
Pregnant and Breastfeeding Women: 600 IU per day
Safety and Risks
While vitamin D is crucial, it’s also important not to take too much. Excessive intake can lead to toxicity, with symptoms like nausea, vomiting, weakness, and serious complications like kidney damage. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen.
Importance of Adequate Vitamin D
Ensuring sufficient vitamin D levels is crucial for bone health, immune function, and overall well-being. While sunlight is a significant source, incorporating vitamin D-rich foods and considering supplements can help maintain optimal levels, especially in cases where sun exposure is limited.
In conclusion, a combination of sunlight, a balanced diet with vitamin D-rich foods, and supplements when necessary can help ensure you get enough of this essential nutrient.