When it comes to sun protection, many people wonder if their sunscreen is effective under extreme conditions, such as in 45-degree hot temperatures. Sunscreen SPF 30 is a popular choice for many, but its effectiveness in high temperatures can raise questions. As the temperature soars to 45 degrees Celsius (113 degrees Fahrenheit), protecting your skin from the sun’s harmful UV rays becomes even more critical. Many people wonder if their SPF 30 sunscreen is up to the task in such extreme heat.
The short answer is yes, SPF 30 sunscreen can be effective in hot weather, but proper application and additional protective measures are essential. This blog will explore whether SPF 30 sunscreen can protect your skin in scorching heat and provide tips on how to use it effectively.
Table of Contents
Understanding SPF
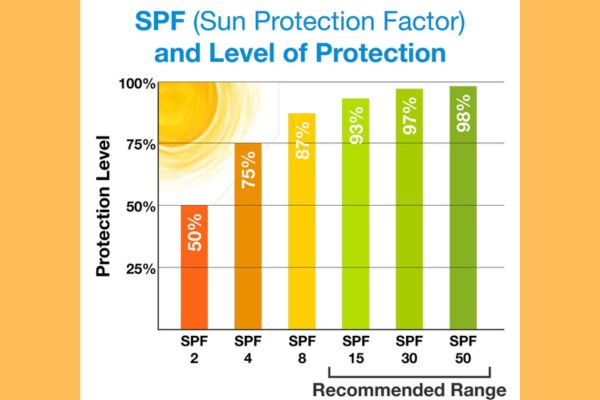
SPF, or Sun Protection Factor, indicates how well a sunscreen can protect the skin from UVB rays, the type of ultraviolet light that causes sunburn and contributes to skin cancer. Here’s what SPF 30 means:
SPF 30: It implies that it would take 30 times longer for your skin to burn with this sunscreen applied than if you were not wearing any sunscreen at all.
Protection Level: SPF 30 blocks approximately 97% of UVB rays.
The Role of Temperature

It’s important to note that the effectiveness of sunscreen is not directly influenced by temperature. Instead, it is determined by the SPF rating and how well it is applied and maintained on the skin. Here are key points to consider:
UV Radiation: The primary factor affecting sunburn and skin damage is UV radiation, not temperature. UV radiation levels can be high on both hot and cold days.
Sweating and Water Exposure: High temperatures can increase sweating, which can wash away sunscreen. This necessitates more frequent reapplication.
Heat Stability: Some sunscreens can degrade in extreme heat, so it’s essential to store them in a cool place and check for any changes in consistency or smell that might indicate degradation.
Effectiveness of SPF 30 in 45-degree Temperatures
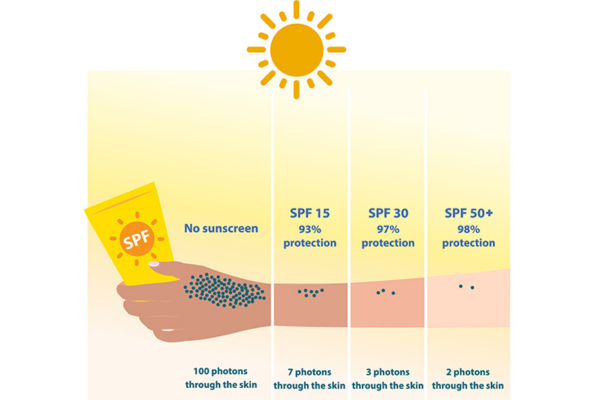
SPF 30 sunscreen remains effective in protecting your skin in 45-degree temperatures, provided it is applied correctly and frequently. Here are some practical tips:
Generous Application: Apply a sufficient amount of sunscreen to all exposed skin. Most adults need about one ounce (a shot glass full) to cover their entire body.
Reapply Regularly: Reapply sunscreen every two hours, or more often if you are sweating heavily or swimming. Water-resistant sunscreens are beneficial, but they still need to be reapplied after 40-80 minutes of water exposure.
Broad-Spectrum Protection: Ensure you are using a broad-spectrum sunscreen, which protects against both UVA and UVB rays. UVA rays can penetrate clouds and glass and contribute to skin aging and cancer.
Additional Sun Protection Measures

While SPF 30 provides good protection, combining it with other sun protection measures can enhance effectiveness, especially in extreme heat:
Seek Shade: Especially during peak sun intensity hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.).
Wear Protective Clothing: Long-sleeved shirts, wide-brimmed hats, and UV-blocking sunglasses can provide additional protection.
Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated, as dehydration can make your skin more susceptible to sunburn.
What is the difference between SPF 30 and SPF 50?
The difference between SPF 30 and SPF 50 lies in the level of protection they offer against UVB rays, which are responsible for causing sunburn and can contribute to skin cancer.

SPF 30 vs. SPF 50
Sun Protection Factor (SPF)
SPF 30: This means that it would take 30 times longer for your skin to burn with this sunscreen applied than if you were not wearing any sunscreen. SPF 30 blocks approximately 97% of UVB rays.
SPF 50: This means that it would take 50 times longer for your skin to burn with this sunscreen applied than if you were not wearing any sunscreen. SPF 50 blocks approximately 98% of UVB rays.
Percentage of UVB Protection
SPF 30: Blocks about 97% of UVB rays.
SPF 50: Blocks about 98% of UVB rays.
While the difference in UVB protection between SPF 30 and SPF 50 might seem minor (1%), it can be significant for people who are highly sensitive to the sun, have fair skin, or are at a higher risk of skin cancer.
Practical Considerations

Reapplication:
Both SPF 30 and SPF 50 sunscreens need to be reapplied every two hours, or more often if you are swimming, sweating, or towel drying.
Proper application is crucial. Most people do not apply enough sunscreen, which can significantly reduce their effectiveness.
Duration of Protection:
SPF does not indicate sun protection but rather the level of protection. Regardless of SPF level, sunscreen should be reapplied every two hours.
Suitability:
SPF 30: Generally sufficient for most people, especially if you’re not spending extended periods in direct sunlight.
SPF 50: Recommended for people with fair skin, those prone to sunburn, individuals spending a lot of time outdoors, or those living in high UV index areas.
Broad-Spectrum Protection:
Ensure the sunscreen you choose provides broad-spectrum protection, meaning it protects against both UVA and UVB rays. UVA rays contribute to skin aging and can also increase skin cancer risk.
Skin Type and Sensitivity:
People with very fair skin, a history of skin cancer, or those undergoing certain medical treatments might benefit more from the higher protection of SPF 50.
Conclusion
SPF 30 sunscreen is effective in protecting your skin from harmful UV rays even in 45-degree hot temperatures. The key to maintaining its effectiveness is proper application and frequent reapplication, especially under conditions that cause sweating or water exposure. Additionally, complementing sunscreen with other protective measures can ensure comprehensive sun safety. Whether it’s a hot summer day or a cooler day with a high UV index, understanding how to use SPF 30 effectively can keep your skin healthy and protected.
Both SPF 30 and SPF 50 sunscreens provide significant protection against UVB rays, with SPF 50 offering slightly more protection than SPF 30. The choice between them should be based on your skin type, sensitivity to the sun, and the conditions you’ll be in. Regardless of the SPF level, proper and regular application is essential to ensure effective sun protection.